1 | <body> |
执行vue-Router.js文件
引入vue-router之前会先引入vue.js文件,执行会生成vue构造函数,
因为vue-router的执行过程会用到vue构造函数这个对象上的方法
当代码引入vue-router.js时,里面相应的代码会执行一遍,
此时vue构造函数已经生成
所以vue-router.js运行后,
不仅会生成vue-router的构造对象
还会调用vue构造函数上的use方法将与router相关的信息挂到vue构造函数对象上
即做一些注册挂载的初始化工作1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55(function (global, factory) {
global.VueRouter = factory());
}(this, function () { 'use strict';
//vue-router的构造对象
var VueRouter = function VueRouter (options) {
if ( options === void 0 ) options = {};
//options即new vueRouter时传进来的参数对象,这里只有一个属性即路由配置对象routes
this.app = null;
this.apps = [];
this.options = options;
this.beforeHooks = [];
this.resolveHooks = [];
this.afterHooks = [];
//该函数会根据路由配合生成路由表,返回两个函数,一个match函数用来匹配路由,另一个addRoutes用来动态增加路由,详见下文具体分析
this.matcher = createMatcher(options.routes || [], this);
var mode = options.mode || 'hash';//路由对象模式,没有配置的话默认初始化为'hash'
//fallback参数用于配置当浏览器不支持 history.pushState 控制路由是否应该回退到 hash 模式
//默认值为 true 官文:https://router.vuejs.org/zh/api/#fallback
this.fallback = mode === 'history' && !supportsPushState && options.fallback !== false;
if (this.fallback) { //history模式下在不支持pushstate方法且配置允许回退hash的情况下回退hash模式
mode = 'hash';
}
if (!inBrowser) { //没有在浏览器中,那应该是在nodejs中,模式重置为abstract
mode = 'abstract';
}
this.mode = mode;//模式确定
switch (mode) { //初始化history对象,三种类型的history构造函数继承自同一父类构造函数History
case 'history':
this.history = new HTML5History(this, options.base);
break
case 'hash':
this.history = new HashHistory(this, options.base, this.fallback);
break
case 'abstract':
this.history = new AbstractHistory(this, options.base);
break
default:
{
assert(false, ("invalid mode: " + mode));
}
}
};
VueRouter.install = install;
VueRouter.version = '3.1.5';
function install (Vue) { } //挂到VueRouter上,被vue.use函数调用
if (inBrowser && window.Vue) { //只在浏览器环境自动挂载,说明在node.js中需要自己调用Vue.use手动挂载
window.Vue.use(VueRouter);
}
return VueRouter;
}));
vue.use 与 VueRouter.install
vue的use方法会调用插件的install方法1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17//在运行initGlobalAPI(Vue)函数时调用initUse挂载到VUE上
Vue.use = function (plugin) {
var installedPlugins = (this._installedPlugins || (this._installedPlugins = []));//this是指Vue哦
if (installedPlugins.indexOf(plugin) > -1) { //避免重复挂载
return this
}
//这个方法会从arguments中取出从第一个数以后的所有参数,这里返回空数组===>[]
var args = toArray(arguments, 1);
args.unshift(this);//this是vue,将vue传给组件进行初始化 ==>[vue]
if (typeof plugin.install === 'function') { //组件定义了plugin.install方法,执行组件plugin.install方法
plugin.install.apply(plugin, args);
} else if (typeof plugin === 'function') { //没定义定义plugin.install方法且组件本身是函数,则调用自身
plugin.apply(null, args);
}
installedPlugins.push(plugin);//将插件推入vue对象上的installedPlugins集合中
return this
};
VueRouter.install方法1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51function install (Vue) { //挂到VueRouter上,被vue.use函数调用
if (install.installed && _Vue === Vue) { return }//避免重复挂载
install.installed = true;
_Vue = Vue;
var isDef = function (v) { return v !== undefined; };
var registerInstance = function (vm, callVal) {
var i = vm.$options._parentVnode;
if (isDef(i) && isDef(i = i.data) && isDef(i = i.registerRouteInstance)) {
i(vm, callVal);//如果定义了registerRouteInstance就执行
}
};
//调用vue.mixin方法 将beforeCreate 和 destroyed,两个生命周期函数存到到对应的钩子函数的集合中
//在执行new vue时会调用callHook执行 beforeCreate相关的钩子函数
//在vue中执行destroyed钩子函数时,同样也会调用这里定义好的生命周期函数
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate: function beforeCreate () { //这里this指向vue
if (isDef(this.$options.router)) {
this._routerRoot = this;
this._router = this.$options.router;
//调用vueRouter对象上的init方法,主要功能是初始化当前路由,设置监听 详见下文
this._router.init(this);
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current);
//defineReactive会对数据进行劫持,进行依赖收集,方便之后页面切换进行监听
} else {//如果没有在new vue时传进vuerouter对象
this._routerRoot = (this.$parent && this.$parent._routerRoot) || this;
}
registerInstance(this, this);
},
destroyed: function destroyed () {
registerInstance(this);
}
});
//访问this.$router,返回new vueRouter生成的对象
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$router', {
get: function get () { return this._routerRoot._router }
});
//访问this.$route,当前页面路由对象 this._router.history.current
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$route', {
get: function get () { return this._routerRoot._route }
});
//挂载RouterView,RouterLink两个组件
Vue.component('RouterView', View);
Vue.component('RouterLink', Link);
//使用vue生命钩子函数合并策略定义路由生命周期钩子函数合并策略 其实就是mergeHook函数
var strats = Vue.config.optionMergeStrategies;
// use the same hook merging strategy for route hooks
strats.beforeRouteEnter = strats.beforeRouteLeave = strats.beforeRouteUpdate = strats.created;
}
小结
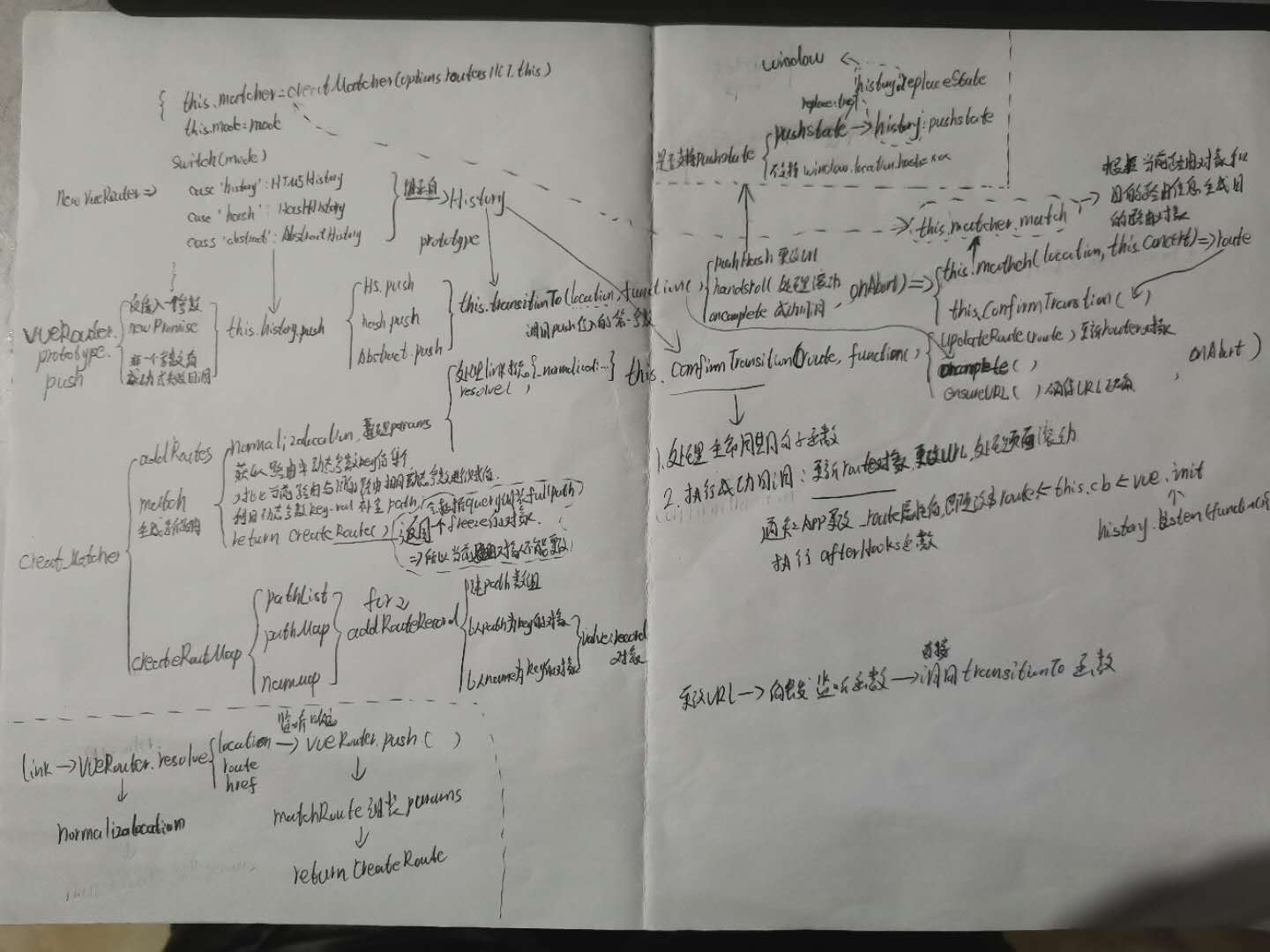
vueRouter在执行阶段会做以下两件事
1.生成vue-router的构造对象
2.挂载vuerouter相关信息到vue对象
挂载到vue对象时会做以下几件事
1.注入两个生命周期函数:beforeCreate和 destroyed
2.指定vue的$router和$route分别指向传进去的vueRouter对象的本身和history.current属性
3.挂载RouterView,RouterLink两个组件
4.指定路由生命周期函数合并策略使用vue中生命周期函数的合并策略
beforeCreate会在new vue时被调用,主要做以下几件事
1.在vue对象上指定与router相关的属性
2.调用vuerouter的init方法,初始化当前路由,设置监听
3.对当前路由进行数据劫持,进行监听
在new vueRouter时,会做以下几件事
1.根据路由配置数组生成路由表,匹配函数以及动态增加路由的函数
2.确定路由模式
3。根据路由模式创建history属性
一个疑惑
当跳转的路由带有query或者params时,将其中的值插入到页面中为什么不会引起XSS攻击?
因为拿到的值类型都是原始js类型,vue在替换值时只是当做字符串替换,不会进行innerHTML
使用js跳转路由
比如this.$router.push({name:foo,query:{id:1}})方法跳转路由
目的页面拿到的query/params数据,就是调用push函数传入的数据
当我们调用push函数时,就是在调用这段代码1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10VueRouter.prototype.push = function push (location, onComplete, onAbort) {
var this$1 = this;
if (!onComplete && !onAbort && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {//进行异步跳转
this$1.history.push(location, resolve, reject);
})
} else {//进行同步跳转
this.history.push(location, onComplete, onAbort);
}
};
location就是我们传入的参数,没有传入 onComplete, onAbort,所以会进入if分支
可见无论进入哪个分支都会调用history对象的push方法
由于在new VueRouter对象时,在构造函数中history是根据传入的选项生成的1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25var mode = options.mode || 'hash';
this.fallback = mode === 'history' && !supportsPushState && options.fallback !== false;
if (this.fallback) {
mode = 'hash';
}
if (!inBrowser) {
mode = 'abstract';
}
this.mode = mode;
switch (mode) {
case 'history':
this.history = new HTML5History(this, options.base);
break
case 'hash':
this.history = new HashHistory(this, options.base, this.fallback);
break
case 'abstract':
this.history = new AbstractHistory(this, options.base);
break
default:
{
assert(false, ("invalid mode: " + mode));
}
}
所以push方法的实现可能为以下三种情况1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38HTML5History.prototype.push = function push (location, onComplete, onAbort) {
var this$1 = this;
var ref = this;
var fromRoute = ref.current;
this.transitionTo(location, function (route) {
pushState(cleanPath(this$1.base + route.fullPath));
handleScroll(this$1.router, route, fromRoute, false);
onComplete && onComplete(route);
}, onAbort);
};
HashHistory.prototype.push = function push (location, onComplete, onAbort) {
var this$1 = this;
var ref = this;
var fromRoute = ref.current;
this.transitionTo(
location,
function (route) {
pushHash(route.fullPath);//更改url
handleScroll(this$1.router, route, fromRoute, false);
onComplete && onComplete(route);
},
onAbort
);
};
AbstractHistory.prototype.push = function push (location, onComplete, onAbort) {
var this$1 = this;
this.transitionTo(
location,
function (route) {
this$1.stack = this$1.stack.slice(0, this$1.index + 1).concat(route);
this$1.index++;
onComplete && onComplete(route);
},
onAbort
);
};
可见三种模式下都会调用共同的父类History上的transitionTo方法
接下来以HashHistory为基础分析接下来的流程
在HashHistory push调用transitionTo时,
传入三个参数:
location 即我们调用push时传入的参数
onAbort 调用push时没有传入,故该值为undefined
第三个参数是一个匿名函数1
2
3
4
5function (route) {
pushHash(route.fullPath);//更改url
handleScroll(this$1.router, route, fromRoute, false);//处理页面滚动相关功能
onComplete && onComplete(route);//调用push时没有传入onComplete,故onComplete=>undefined,不会被执行
},
可见匿名函数内将来要执行pushHash函数
pushHash函数更改浏览器url
1 | function pushHash (path) { |
所以pushHash函数最终的目的是更改浏览器中的url
handleScroll函数处理页面滚动状态,这里暂不做深入
onComplete 值为undefined,故不执行
transitionTo
1 | History.prototype.transitionTo = function transitionTo ( |
transitionTo函数中第一步就是根据根据当前路由信息和传入的目的路由信息生成目的路由对象1
var route = this.router.match(location, this.current);
location 是我们调用push函数传入的参数,
this.current即当前页面路由信息对象
1 | VueRouter.prototype.match = function match ( |
createMatcher
createMatcher函数即创造匹配器的函数,主要做三件事
1.生成路由表
2.生成匹配器,用于将当然路由对象和目的路由信息对象合成目的路由对象
3.生成动态添加路由的函数,因这里可以直接使用路由表1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79function createMatcher (
routes,
router
) {
var ref = createRouteMap(routes);//根据路由配置生成路由表
var pathList = ref.pathList;
var pathMap = ref.pathMap;
var nameMap = ref.nameMap;
function addRoutes (routes) { //动态增加路由
createRouteMap(routes, pathList, pathMap, nameMap);
}
//根据当前路由对象和目的路由信息以及是否重定向等条件合成目的路由对象返回
function match (
raw,
currentRoute,
redirectedFrom
) {
//统一路由参数,合并params给到目的路由
var location = normalizeLocation(raw, currentRoute, false, router);
var name = location.name;
if (name) {//走这条分支
var record = nameMap[name];
{
warn(record, ("Route with name '" + name + "' does not exist"));
}
if (!record) { return _createRoute(null, location) }
var paramNames = record.regex.keys //没有在路由path中配置动态参数,keys数组为空
.filter(function (key) { return !key.optional; })
.map(function (key) { return key.name; });
if (typeof location.params !== 'object') {
location.params = {}; //给location 挂上params
}
if (currentRoute && typeof currentRoute.params === 'object') {
for (var key in currentRoute.params) {//params中有相同key值时,从当前路由将值给到目的路由
if (!(key in location.params) && paramNames.indexOf(key) > -1) {
location.params[key] = currentRoute.params[key];
}
}
}
//如果path有动态参数,使用params将path补全,//以name发起的跳转,挂上了path
location.path = fillParams(record.path, location.params, ("named route \"" + name + "\""));
return _createRoute(record, location, redirectedFrom) 可知返回一route对象
} else if (location.path) { //详见link跳转分析
location.params = {};
for (var i = 0; i < pathList.length; i++) {
var path = pathList[i];
var record$1 = pathMap[path];
if (matchRoute(record$1.regex, location.path, location.params)) {
console.log(location)
return _createRoute(record$1, location, redirectedFrom)
}
}
}
// no match
return _createRoute(null, location)
}
function redirect () {...对重定向一系列的处理,会返回createRoute()}
function alias () {...对路由配置中的别名进行处理,会返回createRoute()}
function _createRoute ( //会生成fullpath
record,
location,
redirectedFrom
) {
if (record && record.redirect) {
return redirect(record, redirectedFrom || location)
}
if (record && record.matchAs) {
return alias(record, location, record.matchAs)
}
return createRoute(record, location, redirectedFrom, router)
}
return {
match: match,
addRoutes: addRoutes
}
}
路由表生成
1 | function createRouteMap ( //生成路由表 |
合并params
在match函数中首先会整理参数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60function normalizeLocation (
raw,
current,
append,
router
) {
//link标签点击传入的raw是to标签指令的值, 为字符串
var next = typeof raw === 'string' ? { path: raw } : raw;
// named target
if (next._normalized) {//已经处理过
return next
} else if (next.name) { //当前调用push使用name标记路由,只会走这个分支
next = extend({}, raw);
var params = next.params;
if (params && typeof params === 'object') {
next.params = extend({}, params);
}
return next
}
// relative params
if (!next.path && next.params && current) {
next = extend({}, next);
next._normalized = true;
var params$1 = extend(extend({}, current.params), next.params);
if (current.name) {
next.name = current.name;
next.params = params$1;
} else if (current.matched.length) {
var rawPath = current.matched[current.matched.length - 1].path;
next.path = fillParams(rawPath, params$1, ("path " + (current.path)));
} else {
warn(false, "relative params navigation requires a current route.");
}
return next
}
var parsedPath = parsePath(next.path || '');
var basePath = (current && current.path) || '/';
var path = parsedPath.path
? resolvePath(parsedPath.path, basePath, append || next.append)
: basePath;
var query = resolveQuery(
parsedPath.query,
next.query,
router && router.options.parseQuery
);
var hash = next.hash || parsedPath.hash;
if (hash && hash.charAt(0) !== '#') {
hash = "#" + hash;
}
return {
_normalized: true,
path: path,
query: query,
hash: hash
}
}
创建路由route对象
1 | function createRoute ( |
所以在调用完match之后会得到route,接着会调用confirmTransition
confirmTransition
1 | 在transitionTo调用时 |
1 | History.prototype.updateRoute = function updateRoute (route) { |
link标签跳转路由
点击link标签时,根据绑定函数即可知道,同样会调用router.push1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30var router = this.$router;
var current = this.$route;
var ref = router.resolve(
this.to,
current,
this.append
);
var location = ref.location;
var route = ref.route;
var href = ref.href;
var handler = function (e) {
if (guardEvent(e)) {
if (this$1.replace) {
router.replace(location, noop);
} else {
router.push(location, noop);//push,直接走同步流程
}
}
};
var on = { click: guardEvent };
if (Array.isArray(this.event)) {
this.event.forEach(function (e) {
on[e] = handler;
});
} else {
on[this.event] = handler;
}
其中,经过resolve处理过的to标签属性的值,会生成统一规范的后续需要使用的location,route1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25VueRouter.prototype.resolve = function resolve (
to,
current,
append
) {
current = current || this.history.current;
var location = normalizeLocation(
to,
current,
append,
this
);
var route = this.match(location, current);
var fullPath = route.redirectedFrom || route.fullPath;
var base = this.history.base;
var href = createHref(base, fullPath, this.mode);
return {
location: location,
route: route,
href: href,
// for backwards compat
normalizedTo: location,
resolved: route
}
};
location 会在normalizeLocation中以第三个return的位置返回如下结构1
2
3
4
5
6{
_normalized: true,
path: path,
query: query,
hash: hash
}
这样相当于提前normalizeLocation调用,所以在match再调用的时候直接返回自身
在接下来的match流程中,会进入以path为依据的流程1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10else if (location.path) {
location.params = {};
for (var i = 0; i < pathList.length; i++) {
var path = pathList[i];
var record$1 = pathMap[path];//根据path拿到record对象
if (matchRoute(record$1.regex, location.path, location.params)) {
return _createRoute(record$1, location, redirectedFrom)
}
}
}
根据标签to赋予的path值,和生成路由表时拿到的path配置值,根据正则表达式解析params对象,
也说明了,为什么跳转路包含动态参数的path时,要跟params配对使用
matchRoute
1 | function matchRoute ( |
直接更改url跳转
在浏览器直接更改含有动态路由的的url,回车跳转,会根据事先绑定的监听事件进行解析处理
在new vue时初始化完当前路由,以执行回调的方式绑定监听1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 VueRouter.prototype.init = function init (app /* Vue component instance */) {
var this$1 = this;
this.app = app;
var history = this.history;
if (history instanceof HTML5History) { //h5history在new h5history时,在构造函数中设置popstate事件监听
history.transitionTo(history.getCurrentLocation());
} else if (history instanceof HashHistory) {
var setupHashListener = function () {
history.setupListeners();//设置监听
};
history.transitionTo( //无论成功与否都绑定
history.getCurrentLocation(),
setupHashListener,
setupHashListener
);
}
history.listen(function (route) { //route改变时调用,this.cb
this$1.apps.forEach(function (app) {
app._route = route;
});
});
};
设置监听具体内容1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30HashHistory.prototype.setupListeners = function setupListeners () {
var this$1 = this;
var router = this.router;
var expectScroll = router.options.scrollBehavior;
var supportsScroll = supportsPushState && expectScroll;
if (supportsScroll) {
setupScroll();
}
window.addEventListener(
supportsPushState ? 'popstate' : 'hashchange',
function () {
var current = this$1.current;
if (!ensureSlash()) {
return
}
//直接调用transitionTo进行路由更新
this$1.transitionTo(getHash(), function (route) { //成功回调不用pushHash更新url
if (supportsScroll) {
handleScroll(this$1.router, route, current, true);
}
if (!supportsPushState) {
replaceHash(route.fullPath);
}
});
}
);
};
可见通过监听事件触发的路由改变会直接调用transitionTo函数进行跳转
两个收获
1.normalizeLocation函数发挥的作用,根据第一参数location对象不同的属性状态进行不同的处理,用于在上游的不同情境(不同方式导致跳转)使用中统一调用
2.在transitionTo函数中调用comfirmTransition,为什么不直接在transitionTo函数中书写confirmTransition函数内容呢,为什么要单独摘出来呢?同样,comfirmTransition函数不止会在transition中调用,
还会在AbstractHistory的go函数中被直接调用,HashHistory和HTML5History的go方法会直接使用window.history.go(n);nodejs全局对象是global,不是windows,所以需要特殊处理